Running and Playing Ethereum DApp Game
Recipe ID: hsts-r46
Self-paced training
We offer blockchain introduction, Hyperledger for system admin, Ethereum, Solidity, Corda R3, Hyperledger for developers, blockchain cybersecurity and more classes in self-paced video format starting at $60. Click here to learn more and register. For complete self-paced blockchain training, visit our Complete Blockchain Development Training page.
Update on Feb 2021
The latest version of this tutorial along with all updated source codes is available via the below link:
https://myhsts.org/blog/ethereum-dapp-with-evm-remix-golang-truffle-and-solidity-part2.html
Recipe Overview
Ethereum is a general-purpose blockchain that is more suited to describing business logic, through advanced scripts, also known as smart contracts. Ethereum was designed with a broader vision, as a decentralized or world computer that attempts to marry the power of the blockchain, as a trust machine, with a Turing-complete contract engine. Although Ethereum borrows many ideas that were initially introduced by bitcoin, there are many divergences between the two.
The Ethereum virtual machine and smart contracts are key elements of Ethereum, and constitute its main attraction. In Ethereum, smart contracts represent a piece of code written in a high-level language (Solidity, LLL, Viper) and stored as bytecode in the blockchain, in order to run reliably in a stack-based virtual machine (Ethereum Virtual Machine), in each node, once invoked. The interactions with smart contract functions happen through transactions on the blockchain network, with their payloads being executed in the Ethereum virtual machine, and the shared blockchain state being updated accordingly.
For those who are not familiar with blockchain technology reading History and Evolution of Blockchain Technology from Bitcoin article is strongly recommended. Also, if you wish to learn and practice Hyperledger blockchain development, visit Comprehensive Hyperledger Training Tutorials page to get the outline of our Hyperledger tutorial articles.
We have written two sets of tutorials to explore Ethereum and Solidity programming in depth. First set covered the following nine recipes:
- Introduction to Ethereum Blockchain Development with DApps and Ethereum VM
- Building Auction DApp With Ethereum and Solidity Programming Language
- Working with Ethereum Blockchain Applications through Remix IDE
- Building Bidding Form in Web3js for Ethereum Auction DApp
- Working with web3js API and JSON to Build Ethereum Blockchain Applications
- Deployment Environments for Managing Ethereum Smart Contracts
- Work with Ethereum Private Network with Golang with Geth
- Compiling and Deploying Ethereum Contracts Using Solidity Compiler
- Running Ethereum Auction DApp and Solidity Tips
In short, you learned about how to set up and configure Ethereum and develop blockchain applications using Solidity programming language. We explored its key components, including smart contracts and Web3.JS API via an Auction Decentralized Application (DApp) step-by-step.
In second set, we discuss more advance topics in Ethereum blockchain development and solidity while building a Tontine DApp game step-by-step. Specifically, we cover Truffle and Drizzle. For instance, we show you how a tool such as Truffle can be an assistant in building, testing, debugging, and deploying DApps. In summary, we are going to cover four main topics:
- Exploring the Truffle suite
- Learning Solidity's advanced features
- Contract testing and debugging
- Building a user interface using Drizzle
The 2nd set consists of 8 recipes as follows:
- Install Truffle and Setup Ganache for Compiling Ethereum Smart Contracts for Tontine DApp Game
- Run Tontine Ethereum DApp Game Contract
- Design Tontine Ethereum DApp Game Interfaces
- Contract Interactions between Ethereum and Solidity via Tontine DApp Game
- Work with Truffle Unit Testing in Tontine DApp Game
- Debugging with Truffle and Ethereum Remix in Tontine DApp Game
- Building Frontend Application for Tontine DApp Game with Drizzle
- Running and Playing Tontine Ethereum DApp Game
IMPORTANT: Understanding and completing the first set of recipes are required prior to working on second set of recipes.
In our first round of recipes, we learned a lot about the Ethereum ecosystem, but we are yet to realize the full potential of its different components. More precisely, we explored how Ethereum works, what a decentralized application (DApp) is and how to build one, and also covered the key concepts of Solidity and web3.js. We then introduced some of the most common smart contract design patterns (withdrawal from a contract, restricting access, state machines), before ending with a discussion of a contract’s cost optimization.
To brush up your knowledge and skills, on second round of recipes, we are going to build a Tontine DApp game. We will exploit this example to explore new tools that are going to change the way you build DApps, and introduce new Solidity features.
In this walkthrough, we will discover how a tool such as Truffle can aid in building, testing, debugging, and deploying our DApp.
The compilation and migration processes are the same as we’ve done multiple times already using the following:
truffle compile-all truffle migrate –reset
Once the contracts are migrated, let’s taste the fruit of our labor in action. In the Drizzle box folder, run the following:
npm run start
The tontine DApp web page comes up immediately in your web browser, as shown here:
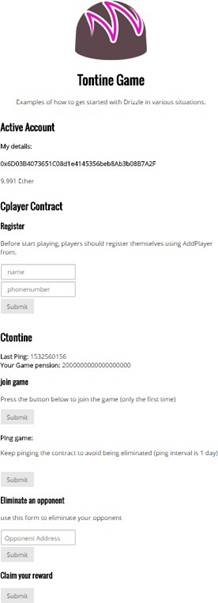
We have got a clean web page with plenty of forms and game details. Eager to play? Let's have some fun!
Showtime – ready to play?
Let’s imagine a scenario where we have two players who are willing to play. We will use a different account for each player from those previously imported into MetaMask.
Afterward, register the first player with details (name, phone number) by filling in the Add
Player form in the game interface, and clicking Submit. A popup will open up in MetaMask, allowing you to submit the transaction. At any time, you can check the transaction status in MetaMask. Wait until it’s marked as Successful:

Then, switch between MetaMask accounts and repeat the same operation to add the second player. Note that each player is identified by their wallet address.
Now, as you have two registered players, you can make them join the Tontine game. Successively, for each account, press the Submit button under join game label:

This time, you’ll get a MetaMask popup showing that you are sending 2 ether to the game (as we fixed that amount in our Drizzle code). Confirm the deposit for both players:
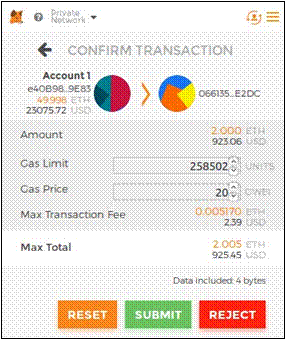

In the same way, you can ping the contract for each player.
I'm sure you’ve noticed that once the join or ping action is dispatched, Drizzle will update the ContractData components (player and Tontine details) automatically without refreshing the whole page as soon the transaction is validated.
As we did in testing, you can increase the time in the trial process to try the elimination feature. From a new Terminal, launch Truffle’s console: truffle console.
This will spawn an interactive console connected to Ganache. We use it to run the following RPC calls:
web3.currentProvider.send({ jsonrpc: "2.0", method: "evm_increaseTime", params: [90000], id: 1 })
web3.currentProvider.send({ jsonrpc: '2.0', method: 'evm_mine', params: [], id:1 })
You can check the block’s timestamp using web3.eth.getBlock("latest").timestamp.
After increasing the time by more than 24 hours, both players can be eliminated. Consider eliminating the second player using the elimination form here:

Once the player is eliminated, Drizzle will automatically display the details at the bottom of the web page:

The remaining player should be able to claim and get the due reward (4 ether). During this tryout, we ensured that the Tontine game is working as expected!
As you can see, we have built a minimalist DApp frontend for the game. This choice was intended to give you the chance to elaborate on the design and create a complete frontend for the game. Count it as an exercise for you. You can even build a small Whisper-based chatroom module for the players. For your information, Whisper (not supported by Ganache) is a direct-messaging protocol in the Ethereum network, and it’s fun to work with. I’ll be waiting for your pull requests.
Getting extra training
Even though we have spent ample time exploring Ethereum and Solidity principles in such a way that you should be able to build DApps, this recipe has its limits and you’ll probably need help at some point. You can register our Ethereum and Solidity programming course for learning Ethereum blockchain development in depth.
Conclustion
An important takeaway from 2nd round of recipes is to think twice before deciding to deploy your final contract and release your DApp. It’s good practice to always plan your contract- development process before jumping into the code, along with conducting thorough testing either using JavaScript or Solidity to ensure quality and security. Keep in mind that writing smart contracts is a critical task as you’ll be dealing with real money. You don’t want your project to end up in the blockchain graveyard. The rule of thumb is begin with testing locally on Ganache, and then on a Testnet before going onto the real Mainnet. Besides this, asking other developers to review your code is always a good habit.
To summarize, we built a Tontine game from scratch and learned new things about Solidity and explored how to use plenty of tools, including Truffle, Remix, and Drizzle, to build a full DApp.
To conclude this recipe, we like to recommend our Learn Hands-on Blockchain Ethereum Development & Get Certified in 30 Hrs, and Become Blockchain Certified Security Architect in 30 hours courses to those interested in pursuing a blockchain development career. This recipe is written by Brian Wu who is our senior Blockchain instructor in Washington DC. His Blockchain By Example book is highly recommended for learning more about blockchain development.
Related Training Courses
Hands-on Node.JS, MongoDB and Express.js Training
Advance JavaScript, jQuery Using JSON and Ajax
Learn Hands-on Blockchain Ethereum Development & Get Certified in 30 Hrs
Learn Blockchain Hyperledger Development & Get Certified in 30 Hrs
Become Blockchain Certified Security Architect in 30 hours
Blockchain Certified Solution Architect in 30 hours
Introduction to Python Programming
Object Oriented Programming with UML
Private and Custom Coding Classes
We offer private coding classes for beginners online and offline (at our Virginia site) with custom curriculum for most of our classes for $59 per hour online or $95 per hour in virginia. Give us a call or submit our Private Coding Classes for Beginners form to discuss your needs.